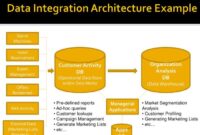
In today’s competitive market landscape, businesses are constantly seeking ways to improve their efficiency and decision-making processes. Two critical concepts that often arise in discussions of business strategy are Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Business Intelligence (BI). While they serve different purposes, the interplay between CRM systems and business intelligence tools can significantly enhance a company’s performance. This article will explore whether CRM qualifies as a business intelligence tool, the differences between the two, and how they can work together to benefit organizations.
What is CRM?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) refers to strategies and technologies used by organizations to manage interactions with current and potential customers. The primary goal of CRM systems is to improve business relationships, streamline processes, and enhance customer satisfaction and retention. Key functionalities of CRM systems include:
- Data Management: Storing customer data, including contact information, purchase history, and preferences.
- Sales Management: Tracking sales leads, opportunities, and pipeline stages.
- Marketing Automation: Automating marketing tasks like email campaigns and lead nurturing.
- Customer Support: Managing customer inquiries, issues, and support tickets to enhance service delivery.
Popular CRM tools include Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM, which offer various features tailored to different business needs.
What is Business Intelligence? <a name=”what-is-business-intelligence”></a>
Business Intelligence (BI) encompasses technologies, applications, and practices used to collect, analyze, and present business data to facilitate informed decision-making. BI tools help organizations transform raw data into meaningful insights through reporting, dashboards, and data visualization. Key components of BI include:
- Data Warehousing: Centralizing data from multiple sources for analysis.
- Data Mining: Extracting patterns and trends from large datasets.
- Reporting and Analysis: Generating reports and visualizations to support strategic decisions.
- Predictive Analytics: Using statistical algorithms to forecast future outcomes based on historical data.
Common BI tools include Tableau, Power BI, and Microsoft Excel, each designed to provide actionable insights that drive business performance.
Is CRM Considered a Business Intelligence Tool?
While CRM systems and business intelligence tools share some overlapping functionalities, it is not entirely accurate to classify CRM as a business intelligence tool. Instead, CRM can be viewed as a component of the broader BI ecosystem. Here’s why:
- Data Collection: CRM systems collect valuable customer data, which can be utilized for business intelligence purposes. However, they primarily focus on managing customer interactions rather than analyzing data for strategic insights.
- Reporting Features: Many modern CRM systems include reporting and analytics features that provide insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness. While this data is useful, it usually lacks the depth of analysis found in dedicated BI tools.
- Integration Capabilities: CRM systems often integrate with BI tools to enhance their analytical capabilities, allowing businesses to leverage customer data in conjunction with other operational data for more comprehensive insights.
In conclusion, while CRM systems possess some features typical of business intelligence tools, they are primarily designed for managing customer relationships rather than providing in-depth business analytics.
The Role of CRM in Business Intelligence
Despite not being classified as a BI tool, CRM plays a crucial role in the business intelligence landscape. Here are some ways in which CRM contributes to BI:
- Customer Insights: By analyzing customer data stored in CRM systems, organizations can gain valuable insights into customer preferences, purchasing behavior, and trends. This information can guide marketing strategies and product development.
- Sales Performance Tracking: CRM systems help track sales activities and performance metrics, enabling businesses to evaluate sales effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
- Segmentation and Targeting: CRM data can facilitate customer segmentation, allowing businesses to tailor marketing campaigns to specific groups based on their behaviors and preferences.
- Feedback Loop: Insights generated from CRM analysis can feed back into the sales and marketing processes, helping organizations refine their strategies based on real-world performance data.
Differences Between CRM and BI
Understanding the distinctions between CRM and BI is essential for organizations looking to enhance their operational efficiency. Here are some key differences:
| Aspect | CRM | Business Intelligence |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Managing customer relationships | Analyzing business data for decision-making |
| Data Types | Customer data, interactions, sales | Operational, financial, market, and customer data |
| Key Features | Contact management, sales tracking | Reporting, dashboards, data visualization |
| End Users | Sales and customer service teams | Analysts, executives, and decision-makers |
| Decision-Making | Short-term, customer-centric decisions | Long-term, strategic decision-making |
Integrating CRM with Business Intelligence
Integrating CRM systems with business intelligence tools can provide organizations with a more comprehensive view of their operations and enhance decision-making. Here’s how to effectively integrate CRM and BI:
- Data Synchronization: Ensure that data from your CRM system is synchronized with your BI tools. This may involve establishing data pipelines or using middleware solutions that facilitate data transfer between systems.
- Custom Dashboards: Create customized dashboards that combine CRM data with other business metrics, allowing decision-makers to visualize performance and gain insights at a glance.
- Automated Reporting: Set up automated reporting features that pull data from both CRM and BI systems, providing regular updates on customer behavior, sales performance, and operational efficiency.
- User Training: Train staff on how to use integrated systems effectively, ensuring they understand how to access and interpret data from both CRM and BI tools.
By leveraging the strengths of both CRM and BI, organizations can make data-driven decisions that enhance customer relationships and overall business performance.
Conclusion
In summary, while CRM systems possess some features commonly associated with business intelligence tools, they primarily focus on managing customer relationships rather than providing comprehensive data analysis. However, when integrated with business intelligence solutions, CRM systems can significantly enhance an organization’s ability to analyze customer data and make informed decisions.
Understanding the roles of CRM and BI, as well as their differences, allows businesses to harness the power of both to drive growth and improve customer satisfaction. Ultimately, the right combination of CRM and business intelligence can lead to improved operational efficiency and a stronger competitive advantage in the market.